How to Test an AVR with a Multimeter? – [Step By Step Guide]
Periodic testing of the AVR will not only save your generator’s vital organs from melting down but also the expensive voltage-sensitive appliances like chargers, UPS, refrigerators, microwaves, etc.
This article aims to provide you with a step-by-step guide about how to test an AVR with a multimeter without hiring a generator mechanic.
What Is AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator)?
AVR is the main organ of the generator to automatically regulates the output voltage so that the appliances can be fed with stable constant power.
The sole purpose of AVR is to control the input from the alternator or generator which is then sent to the voltage-sensitive appliances to protect them from unexpected surges.
Functions of Automatic Voltage Regulators on a Generator
- AVR regulates/maintains the output voltages to ensure that steady excited power should be fed to the voltage-sensitive appliances.
- Provide surge protection against electrical surges or spikes.
- Increase the excitation during any fault to maximize the production of power after clearing the fault.
- Controls the overvoltages due to the sudden losses of the load.
- Separates the reactive loads of the generator with a parallel connection.
How to Test an AVR with a Multimeter?
Tools
Safety Instructions
Testing the AVR of Portable Generators with the Multimeter:
1. Remove the end/stator cover of the generator and disconnect the AVR.
2. Inspect the physical condition.
3. Set the multimeter knob to the OHM (resistance). Also, set the multimeter to the diode option.
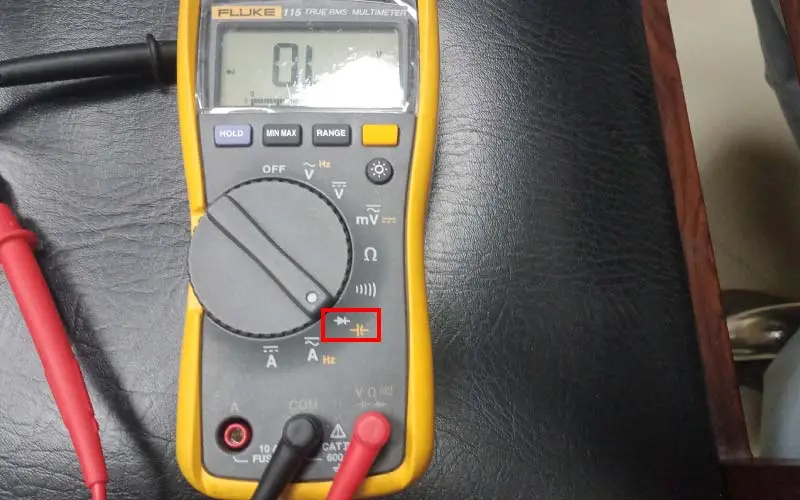

4. Connect the positive terminal of the multimeter to the negative input of the AVR.
5. Take the negative probe of the multimeter and test the output terminals of the AVRs located inside the connector. Make sure to take readings of all 4 terminals.
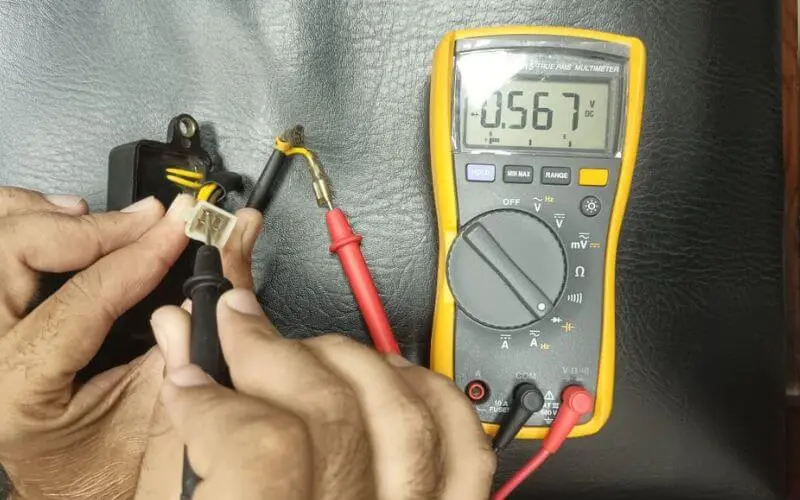

6. Again connect the negative probe of the AVR to the positive terminal of the AVR and take readings as we have done before.
7. If the readings aren’t in thousands or hundreds your Generator’s AVR is fine. A faulty AVR mostly shows the readings in 400, 2000, or 15000, however, a normal AVR shows, between 0.5 to 1.9.
Testing the AVR of Standby Generators with the Multimeter:
1. Locate the AVR of the standby or whole-house generator and disconnect it, most modern generators have an AVR in the control panel or in the alternator’s terminal box.
3. Set the multimeter to the AC voltage and provide the AC (grid) supply to the “L” and “N terminals of the AVR (you can use an extension wire for that). Monitor the AC supply by placing the positive and negative probes on the tip of “L” and “N”, It should be in a stable range.
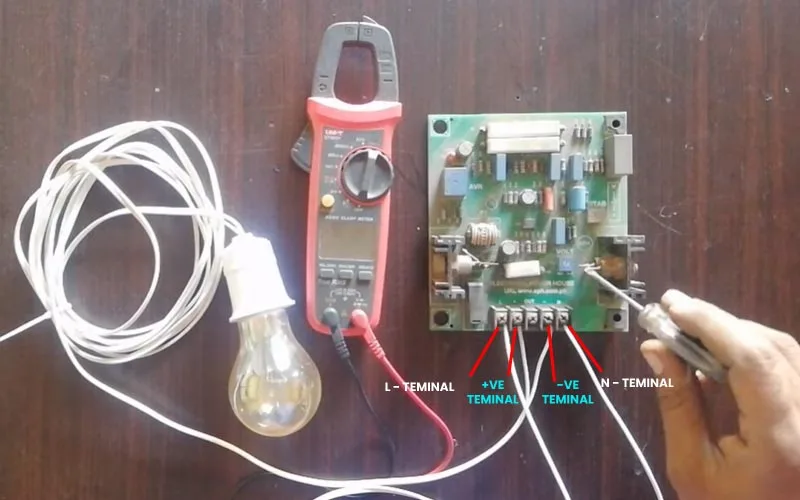
4. Set the multimeter to the DC voltage and place the positive and negative probes on the tip of the positive and negative terminals of the AVR, now rotate the jeweler screw or potentiometer clock or anti-clockwise, If the AVR shows the voltages appropriately on the multimeter and you can adjust it perfectly the AVR is fine.
Recommended Read: How to Adjust Generator Voltage?
How Does a Generator AVR Work?
AVR controls the output voltage by sensing the voltage from the generator terminals and comparing it to a stable reference (calibrated voltages).
What Causes AVR Failure on Generator?
Short Circuit:
Short circuits will not only destroy the generator’s AVR but also other vital organs like windings.
The short circuit is known to be a silent killer for AVRs, they should be examined periodically for not only protecting the voltage regulator but also expensive sensitive appliances.
Variable Speed of Engine:
If the engine is operated at a variable speed, the AVR has to work hard to stabilize the output voltages and as a result, the AVR becomes overloaded or may be damaged in the worst cases.
Sudden Power Changes:
A sudden surge in power may hurt or destroy the AVRs as they are not built to cope with the huge spike in voltage.
Too Old AVR:
Over time the components of the AVR start losing work efficiency and as a result, the AVR starts malfunctioning and needs immediate replacement.
Overload:
The AVR converts the contaminated power to safe and stable electricity so that the expensive appliances can consume steady uncontaminated power.
If the excessive fluctuating power passes through the voltage regulators, they may stop work or even completely fail as they aren’t designed to handle higher loads.
NOTE: An overloaded generator also affects the engine’s speed so the chances are higher that the AVR could malfunction or even complete failure. We recommend diagnosing the generator’s overloading problem should be your first priority.
Improper Fuel Supply:
Improper fuel supply to the combustion chamber of the generator for a long time could overload the AVR.
Dirty Air Filter:
Dirty air filters resist the intake of fresh air and as a result, the generator becomes overheated or backfires with an unsteady power supply that can damage the AVR within no time.
Contact with Water:
As water is the worst enemy of electrical components, if water seeps inside the end/alternator cover of the portable generator, the AVR or winding may be damaged or destroyed.
Excessive Vibrations:
Excessive vibration could shift the wires of the electrical panel and as a result, the AVR starts malfunctioning.
Improper Wiring or Rusted Electrical Panel:
The rusted electrical panel could be the main reason behind the AVR failure, as most of the wiring or main components of the AVR are integrated with the electrical panel. Additionally, improper wiring could also shorten the life of a voltage regulator by shifting the excessive load over the AVR.
How Do I Know If My Voltage Regulator Is Bad?
Fluctuated Voltage: If the generator provides fluctuated voltages (too high or low) your first step is to inspect the AVR if you find any visible damage or irregular voltage readings make sure to replace the AVR immediately.
Generator Produce No Power: As the AVR regulates the output voltages, a malfunctioning or busted AVR could cause your generator to not deliver power.
AVR may not be the only culprit if your generator does not supply power. We have written an in-depth guide about generators not producing power, make sure to have a look to know every possible reason with a solution in detail.
Malfunctioning Instrument Cluster: Instrument clusters of the generator are mostly powered by an AVR, if the instrument cluster fluctuates or has no power the generator may not show the critical readings like fuel, loads, pressure, etc.
Recommended Read: How to Bypass Generator AVR?
When Should I Check the Generator’s AVR?
If the generator produces uneven or no voltage output your first task should be testing the AVR with the help of a multimeter.
How Long Will AVR Last?
The longevity of the AVR is solely dependent on the usage, quality of the AVR, and the surrounding environment/temperature.
As a general rule, a quality AVR with proper maintenance should last for about 4 to 8 years.
We recommend testing the AVR during maintenance; this will not only keep the AVR healthy for a longer time but also drag the costly repairs down the road.
Final Words
If you find the unstable or no voltage, your first task is to test the AVR. A faulty or non-calibrated AVR will be a nightmare for not only the expensive appliances but also the sensors and instrument cluster of the generator.
We encourage doing the testing of the AVR with the help of a multimeter as it doesn’t require super technical knowledge and can be done within a few minutes without spending a penny.
I hope you are now able to do the testing of your faulty automatic voltage regulator with the help of a multimeter, If I have missed something please let me know in the comment section, and I will be more than happy to assist you!
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQS
What Happens if Generator AVR Fails?
If the AVR fails or malfunctions, the generator will lose excitation, and as a result, voltage spikes may be seen and in some cases, the generator may not even provide output power.
How Do I Know If My AVR Is Broken?
You can inspect the physical condition of the AVR and do a test with the help of a multimeter to ensure the AVR isn’t broken from both inside and outside.
What Part of a Generator Controls Voltage?
VR (voltage regulator) or AVR (automatic voltage regulator) is an electrical device that controls the voltage of the current generated by the alternator of the machine. The sole purpose of the voltage regulator is to provide stable power to the sensitive electrical appliances to ensure they last longer.
What Causes Under voltage in Generators?
The generator could produce low voltage for a variety of reasons. One of them is AVR. Checkout our detailed guide about why my generator is providing low voltages?
Can a Generator Run Without AVR?
Yes, but unregulated generators without AVR couldn’t provide stable/safe power, and as a result, we may have to lose our beloved electronics.
Since AVR is the heart of a generator, if it’s damaged/removed deliberately, the generator provides unstable power that can not only harm the generator’s instrument cluster but also the voltage-sensitive appliances.
What Will Happen if AVR is Overloaded?
An overloaded AVR wouldn’t work properly or even completely fail in the worst cases, so make sure to dig deep to know the actual reason for overloading the AVR.
How Does Voltage Regulator Control Generator Voltage?
AVR senses the output of the stator and compares it with the adjusted voltage.

Kashif has been a valuable asset to the electric generator industry for over 5 years. Now, As a skilled energy engineer, he’s been on the front lines of diagnosing problems, fixing broken parts, and performing routine maintenance tasks to keep generators running smoothly.
