Understanding Generator Backfire: 8 Causes and 7 Solutions
The loud popping sound coming out of the exhaust of your generator is backfire. This sound is like a balloon busting or a shotgun firing. Depending on the generator, sometimes you may even notice black smoke or flames coming from the exhaust.
Generator backfire occurs when the air/fuel mixture inside the engine ignites unexpectedly, instead of during the normal power stroke. This sudden release of energy creates a shockwave that can cause the engine to stall, or even cause parts of the engine to break or become damaged.
Why is My Generator Backfiring?

Backfire can be caused by a number of factors, including incorrect carburetor adjustments, poor fuel quality, and improper ignition timing. It can also be caused by a malfunctioning spark plug or a vacuum leak in the intake system.
To prevent backfire and ensure the safe operation of the generator, it is important to properly maintain and service the engine, as well as follow recommended operating procedures.
However, loud pops, black smoke, and flames don’t always mean backfiring, it could be a generator afterfire as well. We will also cover that in our article, but first, let’s get into the detail of generator backfire.
What Causes Generators to Backfire?
The following are reasons for a generator to backfire.
- Lean Air Fuel Mixture in the Carburetor
- Early Combustion
- Faulty Intake Valve
- Low or Old Fuel
- Chocked Lever
- Faulty Fuel Valve
- Clogged Carburetor
- Faulty Spark Plug
1. Lean Air Fuel Mixture in the Carburetor:
For complete combustion, the right amount of air-fuel mixture is needed to pass through the carburetor. The complete combustion exhales carbon dioxide.
However, sometimes lean air-fuel mixture causes slow or incomplete combustion resulting in carbon monoxide which is a colorless, odorless, poisonous gas.
This is what actually happens:
When the power stroke of the piston comes to an end while the combustion process is still in progress, the conditions in the cylinder can change because the piston moves towards the exhaust stroke.
The remaining mixture may become too lean, meaning there is not enough fuel to support continued combustion. This can result in an explosion in the intake or exhaust system, instead of in the combustion chamber, causing backfiring.
In a lean air-fuel mixture, there is not enough fuel to burn completely, leading to unburned fuel and oxygen being expelled through the exhaust system.
When these unburned fuels come into contact with a hot surface, such as the muffler, they can ignite, causing a backfire, flames to come out, or a small explosion (LOUD POP).
2. Early Combustion or Pre-ignition:
Early combustion, also known as pre-ignition, can be a reason for generator backfiring.
Pre-ignition occurs when the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder ignites before the spark plug fires, leading to uncontrolled combustion.
If the intake valve fails to close on time, the combustion of the air-fuel mixture will happen on the combustion plug causing the hot burning fuel and air to move the carburetor by the piston, leading to backfires.
This can cause a knocking or pinging sound, and can also result in backfiring if the flame front reaches the intake or exhaust system.
Pre-ignition can be caused by a number of factors, including a spark that occurs too early, a hot spot in the cylinder, or a lean air-fuel mixture.
The resulting backfire can be loud and damaging to the generator and its components. To prevent pre-ignition and backfire, it is important to maintain the proper air-fuel ratio and keep the generator’s components in good condition.
3. Faulty Intake Valve:

A faulty intake valve can cause a generator to backfire. The intake valves control the flow of air and fuel into the combustion chamber, and if they are not functioning properly.
This can affect the air-fuel mixture and cause incomplete combustion.
A valve that is sticking open or not closing properly can allow air to enter the cylinder at the wrong time, leading to an excessively lean air-fuel mixture and potentially causing backfiring.
This can cause a loud explosion and can potentially damage the generator and its components.
4. Low or Old Fuel:
Low or old fuel can cause a generator to backfire. The fuel in a generator must be in proper condition to provide a precise mix of fuel and air for combustion.
If the fuel is low or has become stale, it can become contaminated with moisture or air, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture.
This can result in a backfire, which is an explosion of the mixture in the intake or exhaust system.
5. Chocked Lever:
Although I am not saying it is always the case, a choked lever can be a potential cause for a generator to backfire.
The choke is a device used to control the air-fuel mixture in the carburetor of a generator, and it’s typically used to help start the engine when it’s cold.
If the choke is set too high, it can result in a rich air-fuel mixture, which can cause a backfire.
When the generator is running, the choke should be gradually adjusted to a lower setting, allowing more air into the carburetor and creating a leaner air-fuel mixture.
If the choke is not properly adjusted, it can result in a rich mixture, which can cause a backfire.
6. Faulty Fuel Valve:
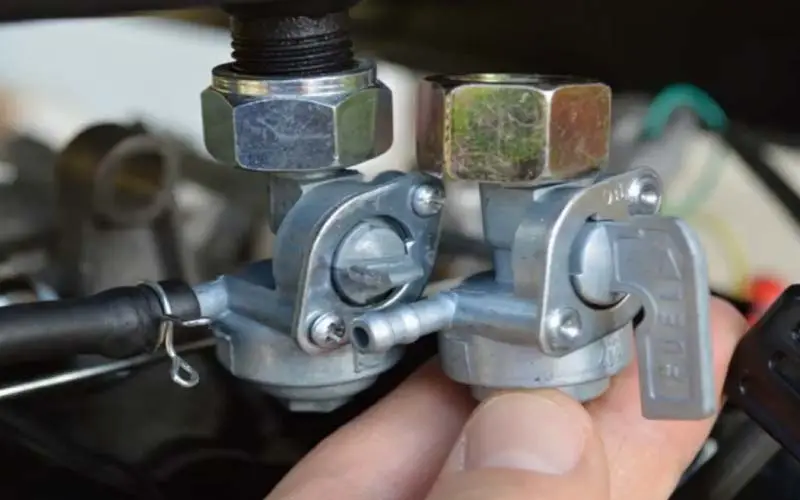
A faulty fuel valve can certainly cause a generator to backfire. The fuel valve controls the flow of fuel into the engine, and if it’s not functioning properly or if it is partially closed, it can cause the air-fuel mixture to become imbalanced, resulting in backfires.
If the fuel valve is stuck open, too much fuel can flow into the engine, causing a rich air-fuel mixture.
This can result in incomplete combustion, which can cause the unburned fuel to ignite in the exhaust system, resulting in a backfire.
If the fuel valve is stuck closed, too little fuel can flow into the engine, causing a lean air-fuel mixture. This can result in the fuel-air mixture being too lean to ignite, causing a backfire.
7. Clogged Carburetor:
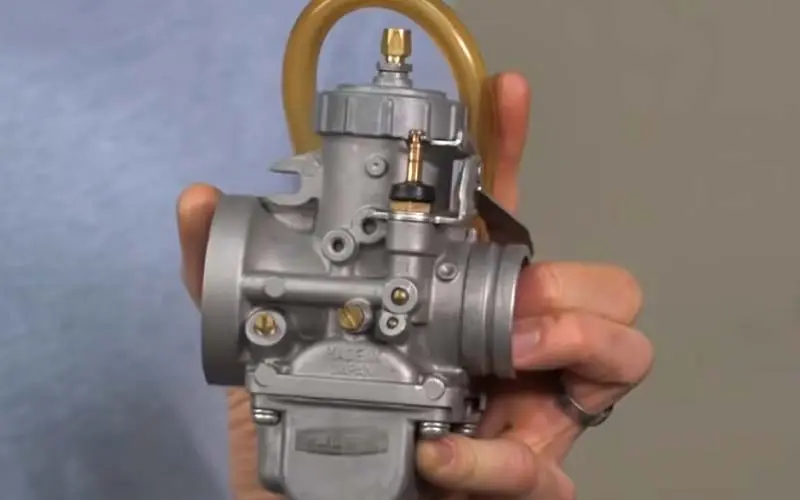
A clogged carburetor is one of the common causes of a generator’s backfire.
The carburetor mixes fuel and air before it enters the engine, and if it becomes clogged, it can disrupt the balance of the air-fuel mixture, causing either a rich or lean mixture. Debris stops the fresh air-fuel mixture to
A rich air-fuel mixture can cause incomplete combustion, leading to unburned fuel igniting in the exhaust system and resulting in a backfire.
A lean air-fuel mixture can result in the fuel-air mixture being too lean to ignite, causing a backfire.
In addition to backfires, a clogged carburetor can also cause other symptoms such as engine stalling, difficulty starting, and reduced engine performance.
8. Faulty Spark Plug:
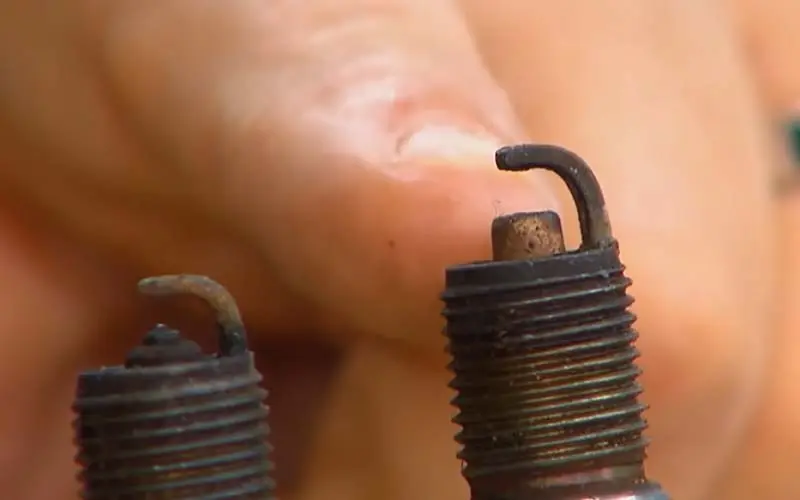

A faulty spark plug can also cause a generator to backfire in most cases. It happens a lot in motorbikes for me.
The spark plug is responsible for igniting the air-fuel mixture in the engine’s combustion chamber. If the spark plug is not functioning properly, the air-fuel mixture may not ignite properly, resulting in a backfire.
A faulty spark plug can cause a variety of issues, including misfires, reduced engine performance, and difficulty starting the generator.
Check this research on engine backfires if you want to know more about the topic.
How to Fix Generator Backfire?
Firstly, you would need to identify the causes behind backfires which are likely to be one of the above-mentioned causes.
Secondly, think before you act. If you feel you can’t repair yourself, call a professional.
Lastly, check if the backfire only happens when you switch off the generator. In that case, it might not need a repair.
Following are the ways to fix a generator backfire.
- Clean Carburetor
- Clean Spark Plug
- Fix Fuel System
- Check the Ignition System
- Fix Exhaust System
- Check for Loose Connections
- Check for Vacuum Leaks
1. Clean Carburetor:
80% of all the problem directly or indirectly comes from the carburetor. A proper cleanup will likely fix your backfiring problem.
For that, you will need to drain the carburetor and clean it using a car cleaner. You got a detailed guide about how to drain a carburetor. Check that out.
2. Clean Spark Plug:
Debris and dirt prevent the spark plug from working properly. It may even cause backfiring. You will either need to replace it or clean it. Check out a detailed article on how to replace a spark plug.
3. Fix the Fuel System:
The first step in fixing a backfiring generator is to check the fuel system. The fuel system can be the cause of backfiring if the carburetor is dirty, clogged, or not adjusted properly.
Clean or replace the carburetor and ensure the correct fuel-to-air ratio. You can do this by adjusting the carburetor’s air/fuel mixture screws until you get the correct ratio.
4. Check the Ignition System:
If the fuel system is not the cause of the backfire, you should then check the ignition system.
The most common cause of backfiring in the ignition system is incorrect timing. The spark plug may also be the cause if it’s worn out, damaged, or not gapped correctly.
Replace the spark plug if necessary and make sure that the timing is set correctly.
5. Fix the Exhaust System:
The exhaust system can also be the cause of backfiring if it’s clogged or restricted.
Make sure that the exhaust pipe and muffler are not clogged and that the engine is getting enough air to run correctly. If necessary, clean or replace the muffler to resolve the issue.
6. Check for Loose Connections:
Make sure that all connections in the generator are tight and secure. Loose connections can cause the generator to backfire, especially in the electrical system.
Check all electrical connections, including the battery cables, spark plug wires, and alternator connections.
7. Check for Vacuum Leaks:
Vacuum leaks can also cause the generator to backfire. A vacuum leak can cause the air-fuel mixture to be incorrect, which can result in backfiring.
Check for vacuum leaks by inspecting the hoses and gaskets in the engine.
Why A Generator Does Backfires When You Shut It Off?
A generator can backfire when it’s shut off due to a buildup of unburned fuel in the engine. It is the residual motion of the piston that ignites the spontaneously combusting air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber.
When the generator is running, the air-fuel mixture is ignited in the combustion chamber, producing energy to power the generator.
However, if the generator is shut off suddenly, the fuel in the engine may not have had a chance to ignite completely, resulting in a buildup of unburned fuel.
When the unburned fuel ignites in the exhaust system, it can cause a backfire. This type of backfire is more common in carbureted engines, as they don’t have the same level of control over the fuel delivery as fuel-injected engines.
What Causes Generators to Afterfire?
After fire in a generator can be caused by a number of factors, including:
1. Lean Air-Fuel Mixture
Just like a backfire, an afterfire can also be caused by a lean-running engine. If the air-fuel mixture is too lean, meaning there is not enough fuel in the mixture, it can result in afterfire.
This can happen because the fuel does not burn completely, leaving unburned fuel that can continue to ignite after the main combustion event has ended.
2. Clogged or Dirty Air Filter
A clogged or dirty air filter can restrict airflow to the engine, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture and afterfire.
3. Delayed Combustion
Just like a backfire, delayed combustion can also cause an afterfire. The spark plug delays its ignition during the piston’s compression phase. The fuel-air mixture burns late as a result.
Now the mixture will burn in during the exhaust stroke. When the mixture reaches the exhaust stroke, it spontaneously combusts using atmospheric oxygen.
4. Fuel Delivery Problems
If there is a problem with the fuel delivery system, such as a clogged fuel filter or a malfunctioning fuel pump, it can cause afterfire. This can happen because the engine is not receiving enough fuel, leading to a lean air-fuel mixture.
5. Incorrect Carburetor Adjustment
If the carburetor is not adjusted correctly, it can result in a lean air-fuel mixture and afterfire.
6. Engine Timing Issues
If the timing of the spark plug is not set correctly, it can cause afterfire. This can happen if the spark plug is firing too late, leading to the ignition of unburned fuel after the main combustion event has ended.
It’s important to address afterfire as soon as possible, as it can result in decreased fuel efficiency and increased emissions.
A trained mechanic should diagnose and repair the root cause of the afterfire to prevent further problems.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
Can a Generator Backfire Damage the Engine?
When a generator backfires, the unburned fuel that ignites in the exhaust system can cause a high-pressure shock wave that can damage the engine.
This shock wave can cause damage to the valves, pistons, and other internal components of the engine. If the backfire is severe enough, it can even cause structural damage to the engine block.
Additionally, the heat generated by the backfire can cause damage to the cylinder head, spark plugs, and other parts of the engine.
Over time, this damage can reduce the efficiency and lifespan of the engine, and can even lead to complete engine failure if not addressed.
To prevent backfiring and engine damage, it’s important to make sure the generator is properly maintained and repaired the oil must be changed on time, the air filter must be cleaned on time, and to address any issues that could be causing the backfire as soon as they arise.

Fareed, the highly skilled electrical expert, boasts 5 years of extensive experience in proficiently maintaining, repairing, diagnosing, and installing a diverse range of electrical systems.
